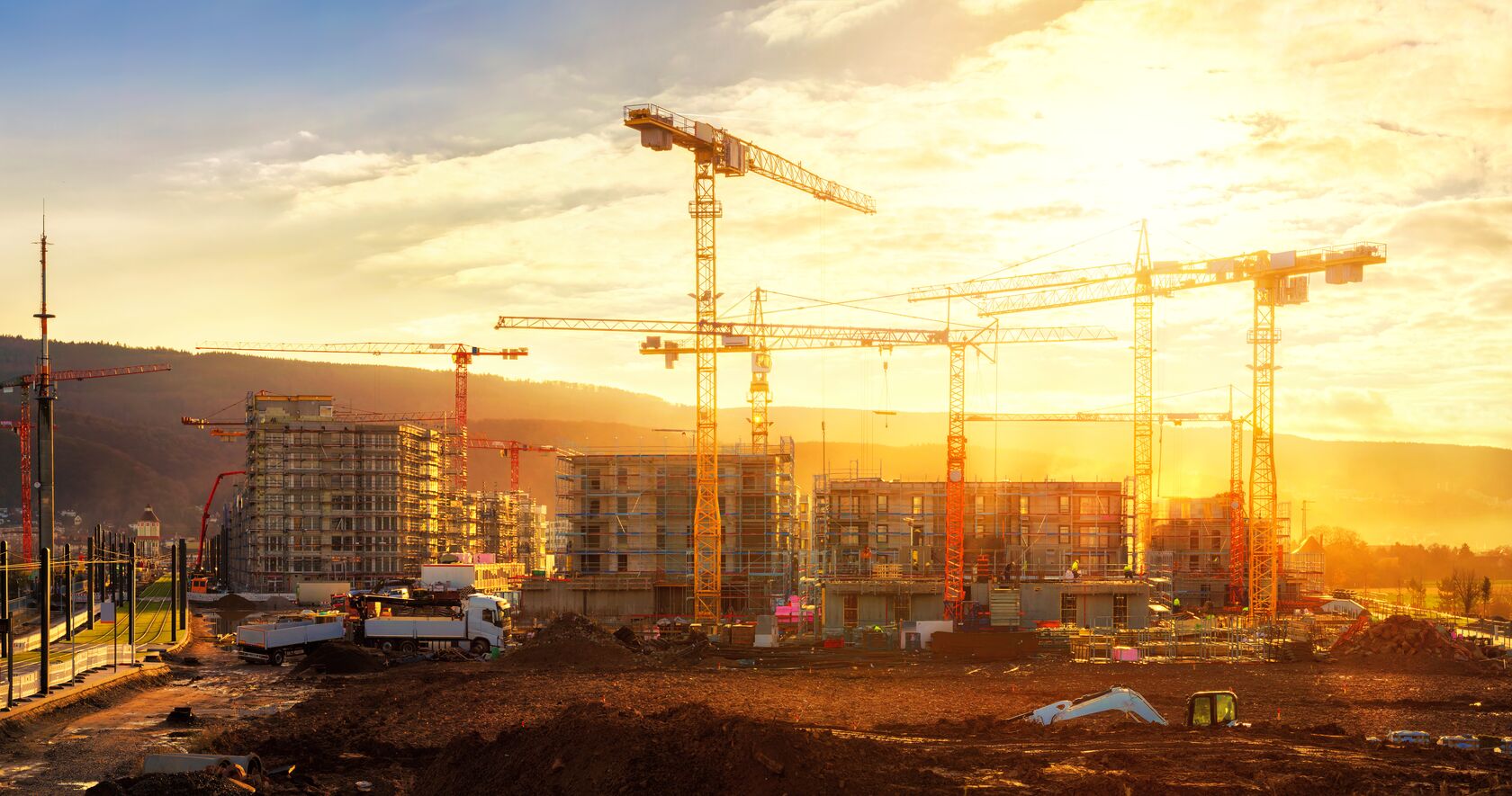
Asset Data Management for Infrastructure Companies
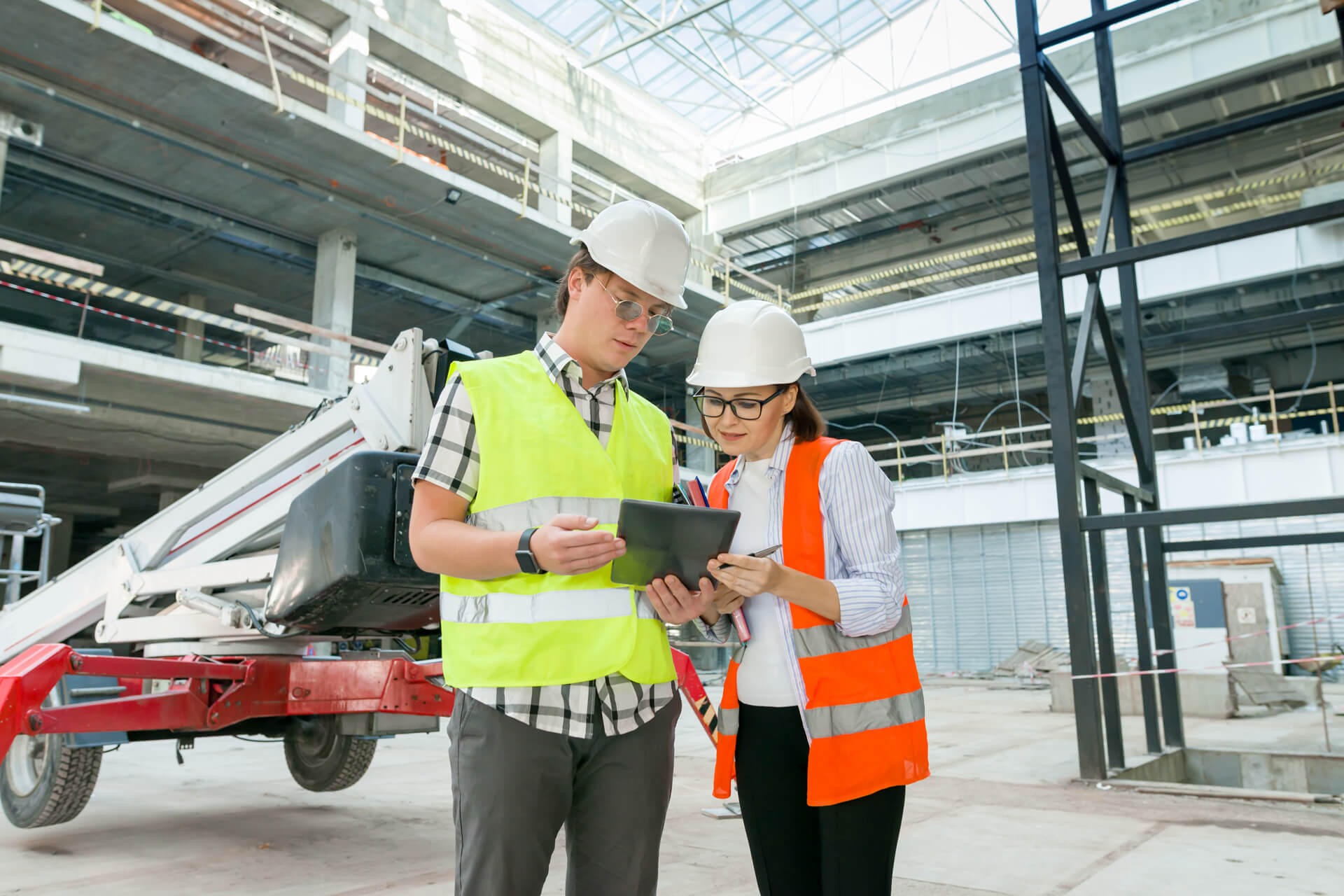

Asset Data Management is the process of acquiring, tracking, utilising, optimising, and leveraging data assets to create value and is a vital task for Infrastructure companies.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) significantly benefit infrastructure companies, and the benefits are not limited to infrastructure design and planning but are also vital tools once the infrastructure is in place.
The role between asset data management and GIS data is both complex and necessary. This article will discuss how GIS is used in asset data management and its many benefits.
What Is the Application of GIS for Infrastructure?
Geographic Information System combines technology, software, and data to capture, manage, analyse and display all types of geographically linked data. GIS technology supports infrastructure organisations to demonstrate, communicate, query and analyse data in several ways.
Spatial data infrastructure (SDI) is a term used for the fundamental set of policies, technologies and organisational structures that enable the availability and accessibility of spatial data. SDI is a foundational component for spatial data discovery, evaluations and application.
Applications for spatial data infrastructure include the following:
- Disaster response
- Land records evaluation
- Water, gas and electric planning
- Public protection
- Defence
- Natural resource management
- Telecommunication networks
How GIS Helps Asset Data Management
Assets are resources or items of value belonging to an infrastructure company or organisation. Integrating a GIS system with asset management creates a cost-effective solution for infrastructure companies and improves the tracking of all assets, not just spatial ones.
GIS is a foundational system that combines technology, software, and data to capture, manage, analyse and display various types of geographically linked data. When utilising asset data management software that connects and supports what is happening in the office and the field, the chances for data inconsistency decrease significantly.
Three sections when viewing a GIS are as follows:
- A system of record. This is where everything about the asset is measured, recorded and tracked, including type, age, location, etc.
- A system of engagement. This is the environment where data is shared with users beyond the leading group of users.
- A system of insight. This platform for analytics and understanding the data supports the decision-making process by providing valuable insight.
Benefits of Asset Data Management for Infrastructure Companies
A GIS-based asset management system with a significant level of transparency improves companies of all sizes’ ability to maintain and manage their assets, including equipment, fleets, facilities, consumables, property and infrastructure, more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Geospatial information and technology make it significantly easier to navigate and understand the precise location of every component of infrastructure, from what’s overhead to what’s underground.
Time and Money
One of the significant benefits of GIS technology is that it offers real-time data both in the field and in the office. Infrastructure planning is critical when it comes to economic development.
GIS tools have become essential in infrastructure development and are highly beneficial, saving operational and administrative time and money. They are vital to improving efficiency and effectiveness in the field of transportation to design, build, improve, and manage the connections and corridors people use daily.
Administrative Use
GIS maps, reports and charts can show infrastructure companies’ patterns, relationships and trends. When integrated with budgeting and project management capabilities, it also supports administration and management. It can be used to track and report maintenance activities using a GIS-based system to improve the efficient scheduling of work tasks, personnel, equipment and inventory costs.
Field Use
Employees in the fields can utilise handheld GIS mobile devices to record data, perform inspections, and locate assets, all in real-time. When a discovery is made in the area, the worker can immediately submit a new service request for repair or maintenance with the GIS device and technology.
Maintain Assets
A significant benefit of asset data management is maintaining asset condition and performance and improving asset longevity.
Collaboration
GIS supports collaboration between project managers and other project participants from various organisations and backgrounds to view and use the data about a project’s progression and improves intelligence decision-making.
When integrated with GIS, asset data management vastly enhances all aspects of infrastructure companies, from the office to the field. With real-time monitoring and extensive data logic, companies can prioritise events to find the best solutions promptly—hiring experts is the best way to maximise the benefits of GIS for your Infrastructure company.
MGISS for Geospatial Consultancy, Software Development, Technical Support and Training
MGISS is here to help you manage networks, future-proof service provision and preempt maintenance needs with intelligent asset management systems. We provide infrastructure companies with extensive data-driven supervision of networks, improving decision-making and efficiency to help mitigate risk and disruptions.
Contact us today to create a solution both in the field and office to save time and money and improve safety and decision-making.
About
Empowering your decision making with the asset data truth. Independently advising on the smarter use of Geospatial data, technology and the digital transformation of field operations.